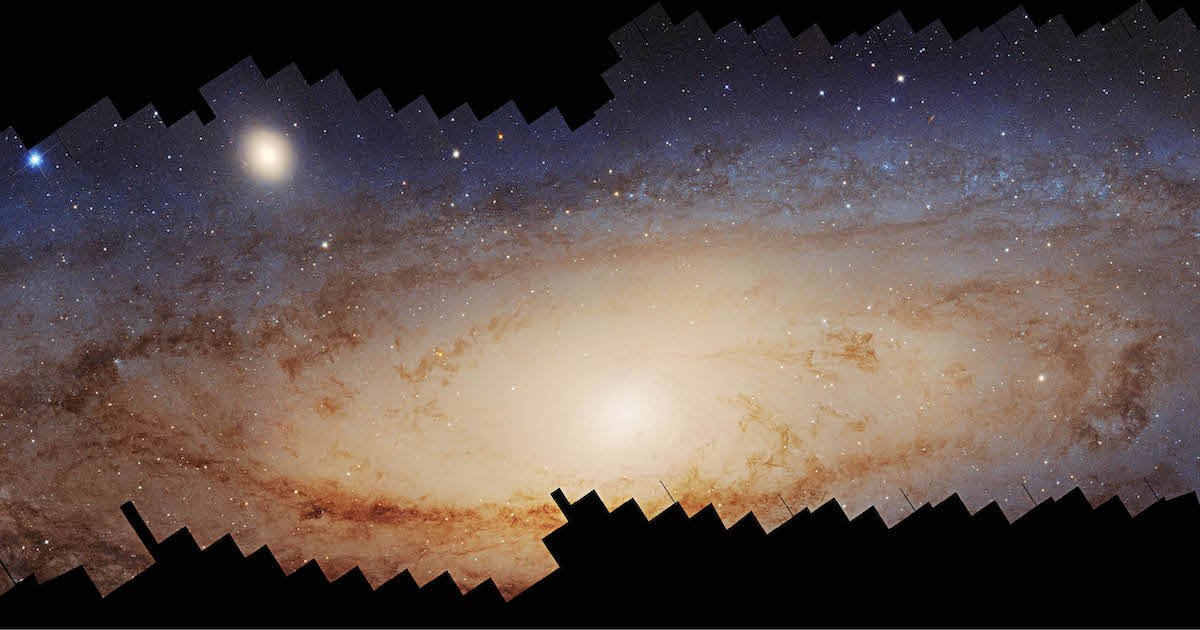

Andromeda Galaxy Panorama Features Over 200 Million Stars


since then Release In 1990, NASA Hubble Space Telescope I have greatly informed our understanding of the universe, taking pictures of the planets in our own solar system and billions of lights of light years. But only earlier this year, the telescope completed one of its most amazing exploits Astronomical photography: 417 megapixel panorama from the Andromeda galaxy.
Galaxy Andromeda is among the closest to Earth, which is 2.5 million light years away from us. In fact, the galaxy is very close, so that it can be seen with a naked eye on clear autumn nights, and appeared “as an object in the form of a faded cigarette almost the angular diameter that appears to our moon,” according to NASA. Nevertheless, Andromeda near was exactly, which made the task of photographing it very difficult.
“The galaxy is a much greater target on the sky than Hubble’s galaxies routinely, which is often billions of light years,” the NASA Hubble Hubble team explained in A. statement.
It is not surprising, then, that the entire composition takes a decade and 1,000 Hubble orbits to complete it. It connects more than 600 overlapping shots, and the panorama works as the largest light assembled ever from the Hubble Space Telescope notes. Via 2.5 billion pixels is a wide and vital set of 200 million stars, and it is just a small part of Andromeda population. If we take it in its entirety, the panorama is not only a technical or photographic achievement, but it is also an important glimpse of Galaxy andromeda itself.
As the nearest neighbor in Milk Way, Andromeda has worked historically as an “agent” of other spiral galaxies in the universe in general, whether it is with regard to its structure or development.
“Without Andromeda as an alternative, astronomers know much less than our milk method,” says NASA. “This is because we are an integral part of the Milky Way. This is like an attempt to understand the planning of New York City by standing in the center of Park.”
“With Hubble we can get into huge details about what is happening on a comprehensive scale across the entire disk in the galaxy. You cannot do this with any other big galaxy.”
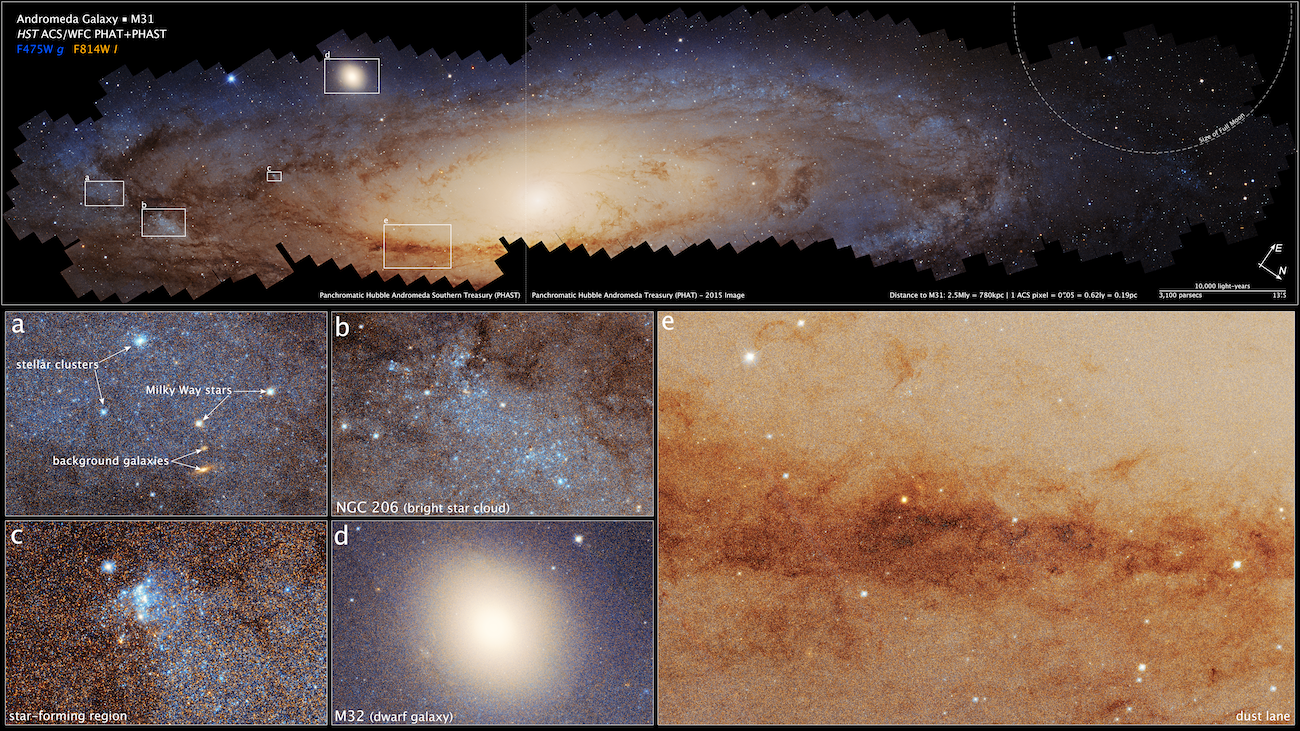
This last panorama started originally with the Hubble Andromeda (PHAT) about 10 years ago, while the northern half of Andromeda was obtained in wavelengths at the level of nearby weapons, visual, and close to infrared using the advanced camera and wide field camera 3 on. PHAT was followed by the Southern Treasury Panthotomi Andromeda (PHAST), which led to additional pictures of about 100 million stars in the southern half of Andromeda. When combining, the PHAT and PHAST collectively cover the full disk of Andromeda.
“This detailed view of the stars that have been resolved in the collection of the history of the previous merger in Galaxy and the date of the interaction,” Williams added.
In NASA, the new results of Hubble will support future notes from the James Web telescope and the upcoming Nancy Grace telescope, which is “a wide version of the corner of the Hubble” and will take “the equivalent of at least 100 high -resolution images in a state of exposure.
To learn more about this unusual panorama of the Andi Underreida, visit NASA website.
Earlier this year, NASA released an incredible Panorama, 417 MB of Andromeda galaxy, which was called the Hubble Space Telescope.
The vast panorama took more than a decade, characterized by 200 million stars.














Post Comment