
New research has revealed the role of Brain Sugar to fight Alzheimer’s disease
NewYou can now listen to Fox News Articles!
The brain contains a hidden “sugar code” that can lead to good treatment for neurological diseases Like Alzheimer’sAccording to new research.
A recently published study in the Journal of Nature Metabolism has found that breaking the brain glycogen (store glucose) can reduce the formation of toxic protein related to normal dementia.
This was the first study indicating that glycogen could actively affect Brain health And Professor of Buck Institute for Research on Edge in California. According to Pankaj Cup, the disease.
Two cancer drugs have promised to reverse the destructive effects of Alzheimer’s
“This study was started by fruit fly (drumophylli), which was revised to imitate Tauopathy, in which the protein called Tau is produced in the brain as it is in the brain,” said Faw News Digital.
The fish used in the study have been damaged by brain and ToddlerAccording to the researcher.

According to the new research, there is a hidden “sugar code” in the brain that can provide good treatment for neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. (ISTOCK)
To ensure that the results can be translated into humans Research squad According to a press release, the patterns of the postmortem brain, as well as the nerve cells created in the lab, were studied by the cells of human patients with the TAU mutation, as well as by people with Alzheimer’s or related conditions.
Study conclusions
In both the fly and human models, researchers have increased the brain glycogen (stored glucose), as well as signs of glycogen breakdown, Capahi told Fox News Digital.
It was an amazing discovery, because the researchers had previously felt that salts were mainly stored in muscles and liver.
The risk of Alzheimer’s can increase with a specific sleep pattern, experts warned
They also found that excess salts contributed to the disease. In scientists’ models, Tau protein interacts with glycogen and prevents it from breaking and loses the ability to stop the loss of nerve cells.
However, researchers found that glycogen phosphorilage (glyep) can reduce the loss of fruit fly and human nerve, which breaks glycogen.
“The next step in the process can make the moving of the potential harmful free radicals that rotate our brain.”
Nerve cells used salts to fight cell damage, indicating that the enzymes responsible for breaking sugar may be promising goals for future treatment.
Researchers were also curious that a Restricted diet The health of the fly can improve the health of the brain.
When they reduced protein content in the diet of insects, the fly was really longer and improved their brain health.
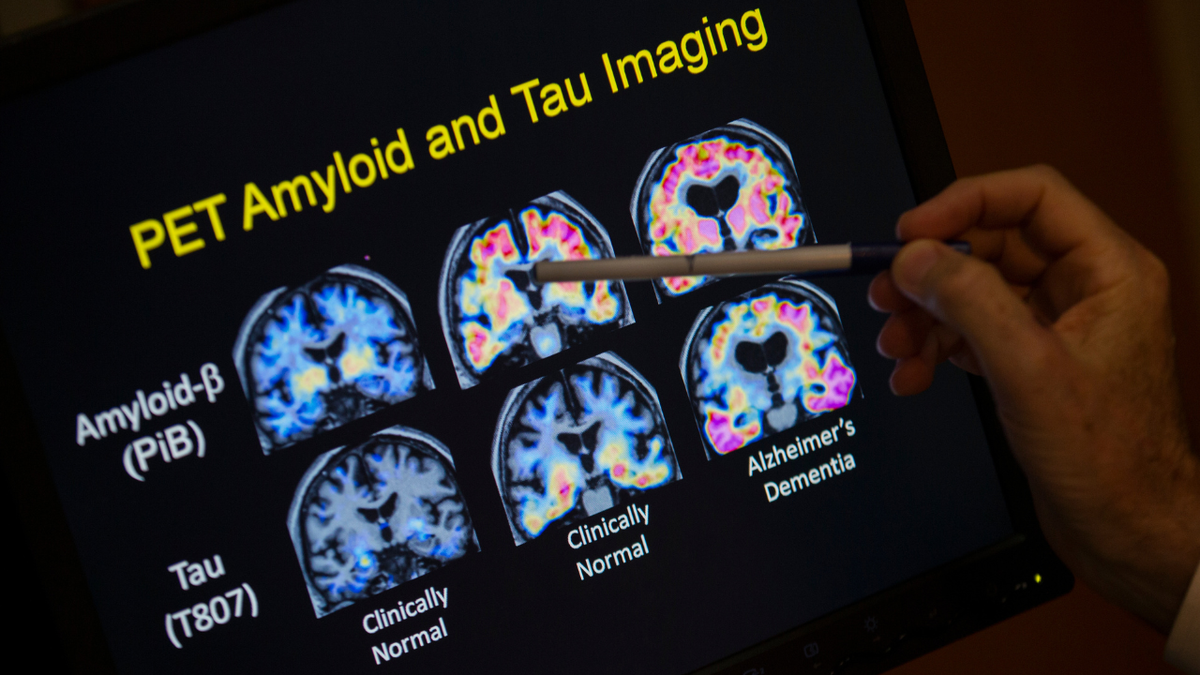
Studies have shown that breaking the brain glycogen (stored glucose) can reduce the production of toxic proteins associated with Alzheimer’s. (AP Photo/Ivan Wochi, File)
“After that, we found that this improvement was linked to the growth of the breakdown of glycogen,” the cup said.
This created the main discovery of the study – that breaking the glycogen in neurons could protect the brain from damage due to the damage caused by the tauus building.
Experts say eating these common substances can reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s
Also Developed a drug Using a special molecule called 8-BR-Camp, the same effect of dietary restrictions was reduced, the press release said.
The authors explained that they still do not recommend a low-proprietary diet-but it is said that this research can pave the way of dietary or drug-based strategies to help Alzheimer’s and related diseases slow down.
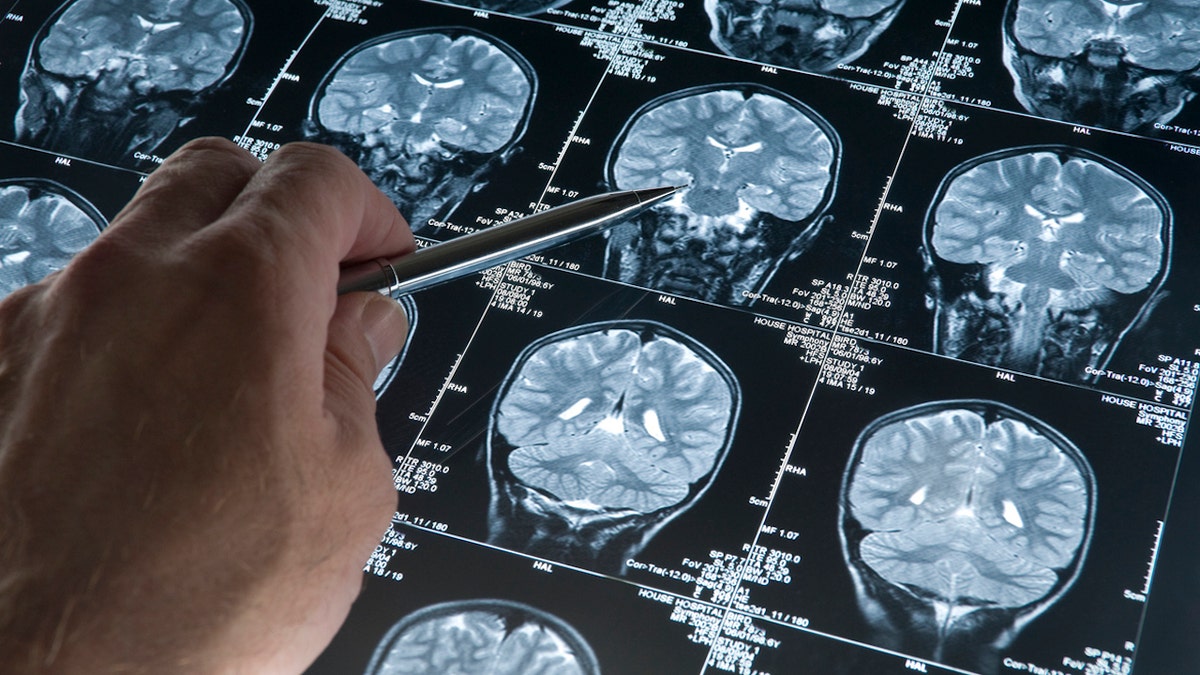
Studies have found that breaking glycogen in neurons can protect the brain from damage due to the damage caused by the taw buildup. (ISTOCK)
Dr. Michael Okun, A Florida neurologist And the medical consultant of the Parkinson’s Foundation did not join the study but commented on the importance of the conclusions.
Click here to get the Fox News app
“Instead of bringing sugar to the energy-burning process, the broken glycogen entered the antioxidant-productive path,” Okun, who is the author of the Parkinson’s plan, “Fox News told Digital.
He said, “The next step in the process can mopping the potentially harmful free radicals that rotate our brain.”

Alzheimer’s disease, the most common type of crazy in the United States, affects more than seven million people in the United States (ISTOCK)
Okun also confirmed that dietary restrictions activated a protective way of the brain and the brain’s sugar deteriorates.
“This finally reduced its loss Alzheimer-related Tau protein, “he said.
Limitation of study
Experts acknowledged that the study, which supports the National Institute of Health, as well as the American Federation of Ageing Research and other sources, has some limitations.
Click here to sign up for our health newspaper
Researchers did not explain whether to break brain glycogen from the death of human brain cells, Okun said.
“We still do not know whether to target the glycogen breakdown in human patients – and most importantly, whether it will be a safe approach.”
“We do not know why glycogen is produced in the disease or it is a reason why Tau Pathology results – although our data indicates that it can increase the disease.”
This research was also done only on fly and human cell models and have not yet been tested on living humans.
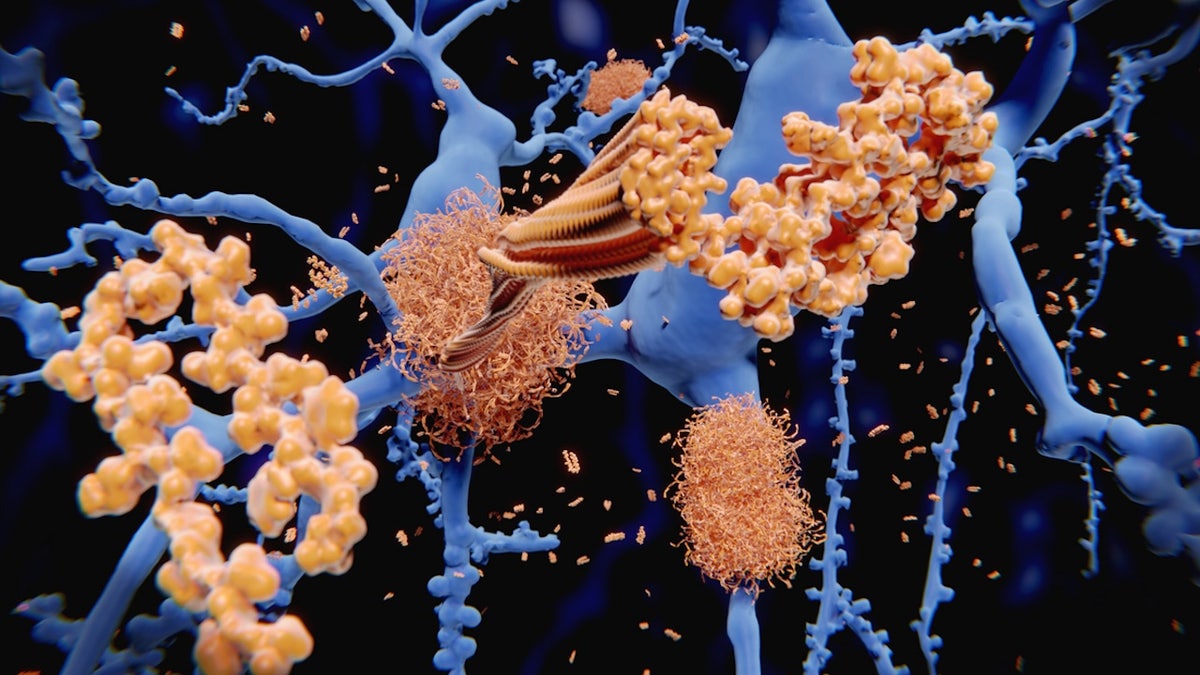
“We do not know why glycogen is produced in the disease or it is a reason why Tau pathology results – although our data indicates that it can increase the disease,” the researcher said. (ISTOCK)
“We still do not know whether the glycogen will work to target the breakdown Human patient – And most importantly, whether it will be a safe view, “Okun said.
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of crazy in the United States, affects more than seven million people in the United States, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
For more health articles, visit www.foxnews.comhhealth
The Neurological disorder Affects memory, thoughts and behavior.
There is no cure for the disease, but some drugs can temporarily reduce progress and improve the quality of life.













Post Comment