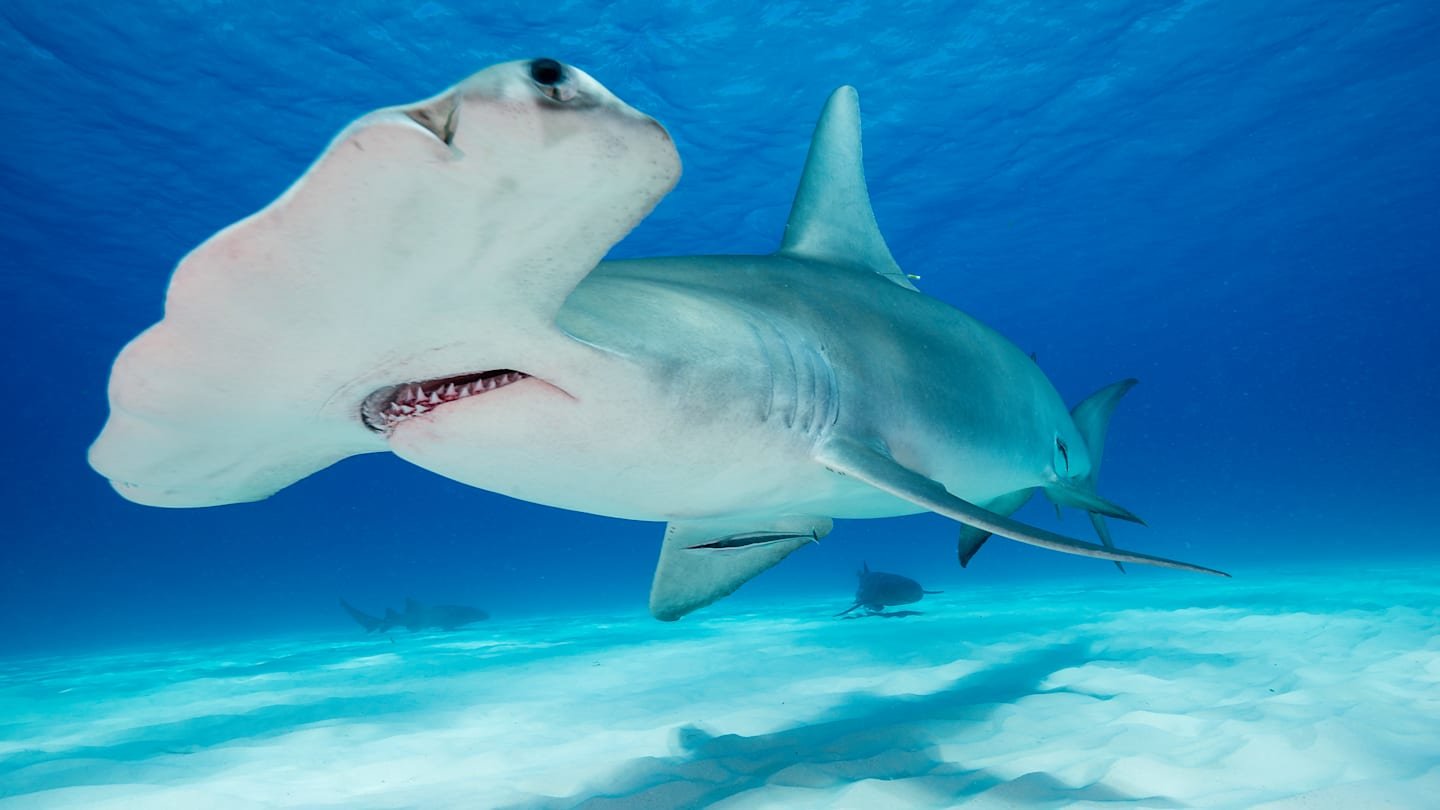

Scientists Have Figured Out Why Hammerheads Love Eating Other Sharks
the Hammer He does not always get the respect he deserves. Thanks to their away cartoon eyes, they usually have a blind spot in front of their hooks as fish schools can gather safely. The placing of the finance often leads to strange tilt to their bodies while swimming. In short, it is the idiot in nature.
Although it may be funny, hammerheads play a high-risk game of hunting other sharks-a desire that science has not yet understood.
Shark World-Eating Shark
in New study Posted in the magazine biologyScientists at the International University of Florida reveal new information about the eating habits of the hammer heads. While most types of sharks adhere to a diet of relatively small and frequent parts, The heads of the hammer tend to search Large black sharks, radiology and baracoda that require great energy to follow up and digest. (The head of the hammer may weigh 250 lbs; the researchers wanted 55 pounds.
For answers, nine heads of the Gulf and Atlantic coasts were held in Florida and equipped with biological sensors that measure the speed and location of shark swimming. The cameras were able to take a video of their environment. Then they returned to the water, where researchers can monitor the predatory activities of the hammer and track the metabolism.
While searching for Blacktip fishing has requested a lot of energy, the payment was worth it. It means Blacktip rupping, which has an area of 55 pounds, which reaches approximately 20 to 25 percent of its body weight, that the hammer head can meet energy requirements during the next three weeks. This amount of meticulous voltage is less than the continuous energy that spends a much smaller coral reef prey on the basis of every day or daily.
When food is particularly rare, it is possible that one meal of Blacktip Binge may maintain the head of the hammer for two months, providing it with a complement to the daily feed of small fish (0.5 pounds). The heads of the hammer also tend to fodder in time, as black hunt in the winter when the species are more abundant and thus easier to locate their location.
Why is the data important
Wonderful sharks are classified as a type of endangered species, which makes understanding that it needs to survive to obtain preservation strategies.
“In order to help protect endangered species such as the great hammer heads, we need to understand their basic biology and how they interact with their environment.” Irene Spencer, PhD In a statement. “It is important to continue to study these big questions, especially in the face of the changing environment.”
This shark has larger fish to fry. | Gerard Soury/Gettyimages The research was also successful in measuring traditional traditional marine species. Unlike wild animals, wild wildlife monitoring can be a logistical nightmare. Biology – in this case, with sensors associated with a dorsal shark – can provide high -quality data on metabolic needs. It is evidence that the hammer heads use energy wisely in consuming 25 percent of its mass at one time, compared to the types of sharks that may consume 5 percent or less. This is not the first FIU exploration of the hammer heads. In 2024,
The researchers found That a kind of hammerhead, Bonnethead stood up, holds certain areas off the Colombian coast. By isolating their geographical preferences, conservative specialists can suggest protected areas called “unavailable areas” where species cannot be captured or removed. The heads of the hammer can still appear in unexpected places. In June, one of Bonnethead
Decrease
On the Golf Court in Mertel Beach, South Carolina. Osbury had brought her up after her attack by two crows.













Post Comment